Pre-State Israel: The Arabs in Palestine
by Mitchel Bard
 Click to enlarge |
For many centuries, Palestine was a sparsely populated, poorly cultivated, and widely-neglected expanse of eroded hills, sandy deserts and malarial marshes. Mark Twain, who visited Palestine in 1867, described it as: “...[a] desolate country whose soil is rich enough, but is given over wholly to weeds-a silent mournful expanse....A desolation is here that not even imagination can grace with the pomp of life and action....We never saw a human being on the whole route....There was hardly a tree or a shrub anywhere. Even the olive and the cactus, those fast friends of the worthless soil, had almost deserted the country.”
During the Annual General Meeting of the PEF in 1875, the Earl of Shaftesbury said of Palestine, “We have there a land teeming with fertility and rich in history, but almost without an inhabitant – a country without a people, and look! scattered over the world, a people without a country.”
As late as 1880, the American consul in Jerusalem reported the area was continuing its historic decline. “The population and wealth of Palestine has not increased during the last forty years,” he said.
The Report of the Palestine Royal Commission quotes an account of the Maritime Plain in 1913:
Lewis French, the British Director of Development wrote of Palestine:
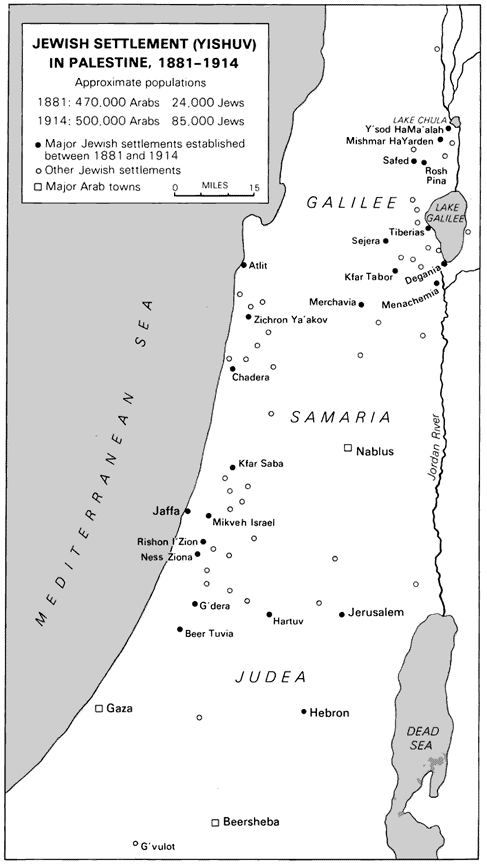
The Arab population at the time was approximately 600,000 compared to 94,000 Jews.
Surprisingly, many people who were not sympathetic to the Zionist cause believed the Jews would improve the condition of Palestinian Arabs. For example, Dawood Barakat, editor of the Egyptian paper Al-Ahram, wrote: “It is absolutely necessary that an entente be made between the Zionists and Arabs, because the war of words can only do evil. The Zionists are necessary for the country: The money which they will bring, their knowledge and intelligence, and the industriousness which characterizes them will contribute without doubt to the regeneration of the country.”
Even a leading Arab nationalist believed the return of the Jews to their homeland would help resuscitate the country. According to Sherif Hussein, the guardian of the Islamic Holy Places in Arabia:
A Population Boom
As Hussein foresaw, the regeneration of Palestine, and the growth of its population, came only after Jews returned in massive numbers. The Jewish population increased by 470,000 between World War I and World War II while the non-Jewish population rose by 588,000. In fact, the permanent Arab population increased 120 percent between 1922 and 1947 to more than 1.3 million.
This rapid growth was a result of several factors. One was immigration from neighboring states – constituting 37 percent of the total immigration to pre-state Israel – by Arabs who wanted to take advantage of the higher standard of living the Jews had made possible. The Arab population also grew because of the improved living conditions created by the Jews as they drained malarial swamps and brought improved sanitation and health care to the region. Thus, for example, the Muslim infant mortality rate fell from 201 per thousand in 1925 to 94 per thousand in 1945 and life expectancy rose from 37 years in 1926 to 49 in 1943.
The Arab population increased the most in cities with large Jewish populations that had created new economic opportunities. From 1922-1947, the non-Jewish population increased 290 percent in Haifa, 131 percent in Jerusalem, and 158 percent in Jaffa. The growth in Arab towns was more modest: 42 percent in Nablus, 78 percent in Jenin and 37 percent in Bethlehem.
Jewish Land Purchases
Despite the growth in their population, the Arabs continued to assert they were being displaced. The truth is from the beginning of World War I, part of Palestine’s land was owned by absentee landlords who lived in Cairo, Damascus and Beirut. About 80 percent of the Palestinian Arabs were debt-ridden peasants, semi-nomads and Bedouins.
Jews went out of their way to avoid purchasing land in areas where Arabs might be displaced. They sought land that was largely uncultivated, swampy, cheap and, most important, without tenants. In 1920, Labor Zionist leader David Ben-Gurion expressed his concern about the Arab fellahin, whom he viewed as “the most important asset of the native population.” Ben-Gurion said, “under no circumstances must we touch land belonging to fellahs or worked by them.” He advocated helping liberate them from their oppressors. “Only if a fellah leaves his place of settlement,” Ben-Gurion added, “should we offer to buy his land, at an appropriate price.”
It was only after the Jews had bought all this available land that they began to purchase cultivated land. Many Arabs were willing to sell because of the migration to coastal towns and because they needed money to invest in the citrus industry.
When John Hope Simpson arrived in Palestine in May 1930, he observed: “They [Jews] paid high prices for the land, and in addition they paid to certain of the occupants of those lands a considerable amount of money which they were not legally bound to pay.”
In 1931, Lewis French conducted a survey of landlessness and eventually offered new plots to any Arabs who had been “dispossessed.” British officials received more than 3,000 applications, of which 80 percent were ruled invalid by the Government’s legal adviser because the applicants were not landless Arabs. This left only about 600 landless Arabs, 100 of whom accepted the Government land offer.
In April 1936, a new outbreak of Arab attacks on Jews was instigated by a Syrian guerrilla named Fawzi al-Qawukji, the commander of the Arab Liberation Army. By November, when the British finally sent a new commission headed by Lord Peel to investigate, 89 Jews had been killed and more than 300 wounded.
The Peel Commission’s report found that Arab complaints about Jewish land acquisition were baseless. It pointed out that “much of the land now carrying orange groves was sand dunes or swamp and uncultivated when it was purchased....there was at the time of the earlier sales little evidence that the owners possessed either the resources or training needed to develop the land.” Moreover, the Commission found the shortage was “due less to the amount of land acquired by Jews than to the increase in the Arab population.” The report concluded that the presence of Jews in Palestine, along with the work of the British Administration, had resulted in higher wages, an improved standard of living and ample employment opportunities.
In his memoirs, Transjordan’s King Abdullah wrote:
Even at the height of the Arab revolt in 1938, the British High Commissioner for Palestine believed the Arab landowners were complaining about sales to Jews to drive up prices for lands they wished to sell. Many Arab landowners had been so terrorized by Arab rebels they decided to leave Palestine and sell their property to the Jews.
The Jews were paying exorbitant prices to wealthy landowners for small tracts of arid land. “In 1944, Jews paid between $1,000 and $1,100 per acre in Palestine, mostly for arid or semiarid land; in the same year, rich black soil in Iowa was selling for about $110 per acre.”
By 1947, Jewish holdings in Palestine amounted to about 463,000 acres. Approximately 45,000 of these acres were acquired from the Mandatory Government; 30,000 were bought from various churches and 387,500 were purchased from Arabs. Analyses of land purchases from 1880 to 1948 show that 73 percent of Jewish plots were purchased from large landowners, not poor fellahin. Those who sold land included the mayors of Gaza, Jerusalem, and Jaffa. As’ad Shuqeiri, a Muslim religious scholar and father of the first PLO chairman, Ahmad Shuqeiri, took Jewish money for his land. Even King Abdullah leased land to the Jews. In fact, many leaders of the Arab nationalist movement, including members of the Muslim Supreme Council, sold land to Jews.


